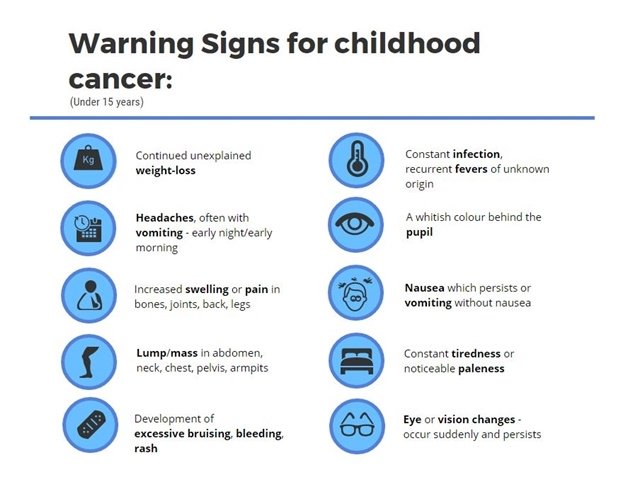

Find out about the possible symptoms of childhood cancer and when your child might be referred to see a specialist.
Cancer symptoms can be very similar to those of other childhood illnesses. And they vary between children. Remember the symptoms we list here are not usually cancer.
See your doctor if your child has any of these symptoms:
- Unable to wee, or has blood in their wee
- An unexplained lump, firmness or selling any where in their body
- Persistent abdominal pain or swelling
- Back pain or bony pain that doesn’t go away
- Unexplained seizures or changes in behaviour
- Headaches that don’t go away
- Frequent or unexplained bruising, unusual paleness or a rash of small red or purple spots that cant’t be explained
- Unexplained bleeding
- Feeling tired all the time
- Frequent infections or flu-like symptoms
- Unexplained vomiting (being sick)
- Unexplained fever (high temperatures) or sweating
- Unexplained weight loss
- Feeling short of breaht
- Changes in appearance of the eye or unusual eye reflections in photos
Cancers that Develop in Children
The types of cancers that occur most often in children are different from those seen in adults. The most common cancers of children are:
- Leukemia
- Brain and spinal cord tumors
- Neuroblastoma
- Wilms tumor
- Lymphoma (including both Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin)
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Retinoblastoma
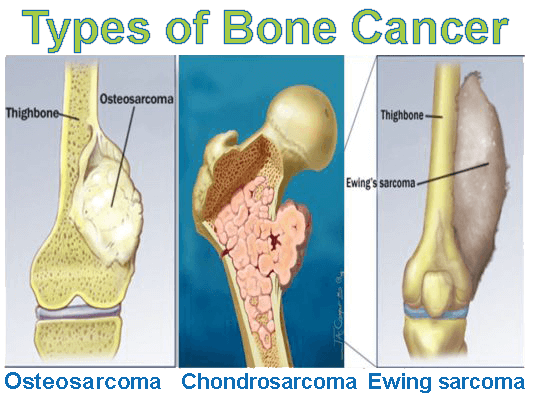
- Bone cancer (including osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma)
Other types of cancers are rare in children, but they do happen sometimes. In very rare cases, children may even develop cancers that are much more common in adults.
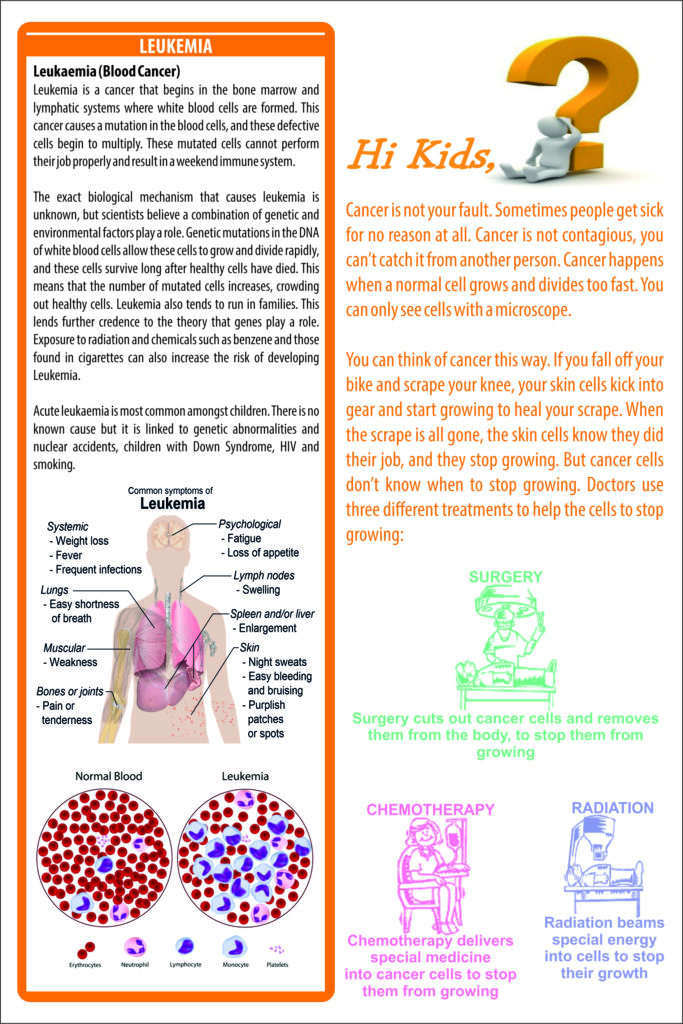
Leukemia
Leukemias, which are cancers of the bone marrow and blood, are the most common childhood cancers. They account for about 30% of all cancers in children. The most common types in children are acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). These leukemias can cause bone and joint pain, fatigue, weakness, pale skin, bleeding or bruising, fever, weight loss, and other symptoms. Acute leukemias can grow quickly, so they need to be treated (typically with chemotherapy) as soon as they are found.
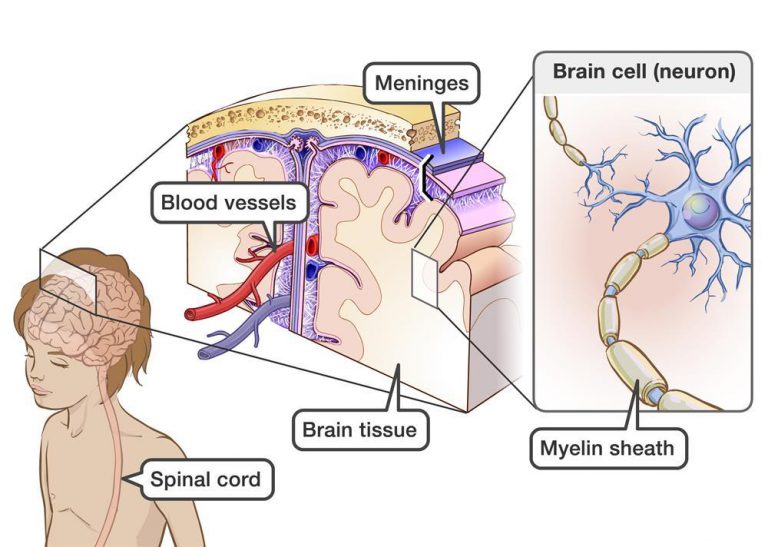
Brain and spinal cord tumors
Brain and central nervous system tumors are the second most common cancers in children, making up about 26% of childhood cancers. There are many types of brain tumors, and the treatment and outlook for each is different.
Most brain tumors in children start in the lower parts of the brain, such as the cerebellum or brain stem. They can cause headaches, nausea, vomiting, blurred or double vision, dizziness, seizures, trouble walking or handling objects, and other symptoms. Adults are more likely to develop tumors in upper parts of the brain. Spinal cord tumors are less common than brain tumors in both children and adults.
Neuroblastoma
Neuroblastoma starts in early forms of nerve cells found in a developing embryo or fetus. About 6% of childhood cancers are neuroblastomas. This type of cancer develops in infants and young children. It is rarely found in children older than 10. The tumor can start anywhere but usually starts in the belly (abdomen) where it is noticed as swelling. It can also cause bone pain and fever.
Wilms tumor
Wilms tumor (also called nephroblastoma) starts in one, or rarely, both kidneys. It is most often found in children about 3 to 4 years old, and is uncommon in children older than age 6. It can show up as a swelling or lump in the belly (abdomen). Sometimes the child might have other symptoms, like fever, pain, nausea, or poor appetite. Wilms tumor accounts for about 5% of childhood cancers.
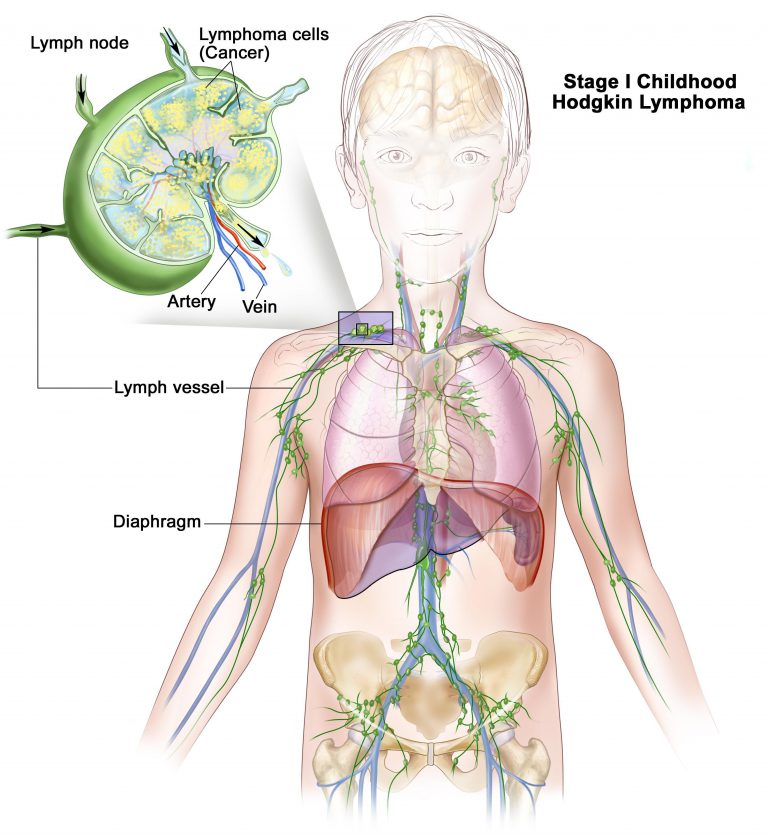
Lymphomas
Lymphomas start in immune system cells called lymphocytes. They most often start in lymph nodes and other lymph tissues, like the tonsils or thymus. These cancers can also affect the bone marrow and other organs. Symptoms depend on where the cancer is and can include weight loss, fever, sweats, tiredness (fatigue), and lumps (swollen lymph nodes) under the skin in the neck, armpit, or groin.
The 2 main types of lymphoma are Hodgkin lymphoma (sometimes called Hodgkin disease) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Both types occur in children and adults.
Hodgkin lymphoma accounts for about 3% of childhood cancers. It is more common, though, in early adulthood (age 15 to 40, usually people in their 20s) and late adulthood (after age 55). Hodgkin lymphoma is rare in children younger than 5 years of age. This type of cancer is very similar in children and adults, including which types of treatment work best.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma makes up about 5% of childhood cancers. It is more likely to occur in younger children than Hodgkin lymphoma, but it is still rare in children younger than 3. The most common types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children are different from those in adults. These cancers often grow quickly and require intensive treatment, but they also tend to respond better to treatment than most non-Hodgkin lymphomas in adults.
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma starts in cells that normally develop into skeletal muscles. (These are the muscles that we control to move parts of our body.) This type of cancer can start nearly any place in the body, including the head and neck, groin, belly (abdomen), pelvis, or in an arm or leg. It may cause pain, swelling (a lump), or both. This is the most common type of soft tissue sarcoma in children. It makes up about 3% of childhood cancers.
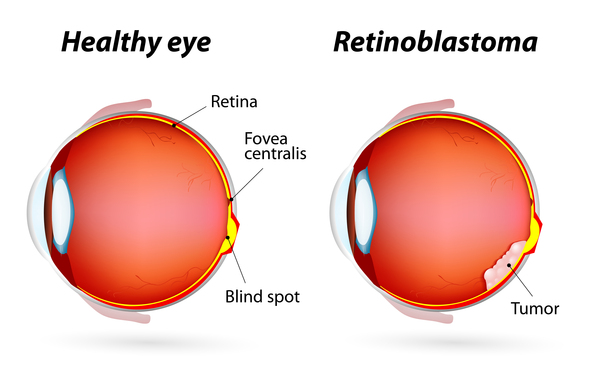
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a cancer of the eye. It accounts for about 2% of childhood cancers. It usually occurs in children around the age of 2, and is seldom found in children older than 6. Retinoblastomas are usually found because a parent or doctor notices a child’s eye looks unusual. Normally when you shine a light in a child’s eye, the pupil (the dark spot in the center of the eye) looks red because of the blood in vessels in the back of the eye. In an eye with retinoblastoma, the pupil often looks white or pink. This white glare of the eye may be noticed after a flash picture is taken.
Bone cancers
Cancers that start in the bones (primary bone cancers) occur most often in older children and teens, but they can develop at any age. They account for about 3% of childhood cancers.
Two main types of primary bone cancers occur in children:
Osteosarcoma is most common in teens, and usually develops in areas where the bone is growing quickly, such as near the ends of the long bones in the legs or arms. It often causes bone pain that gets worse at night or with activity. It can also cause swelling in the area around the bone.
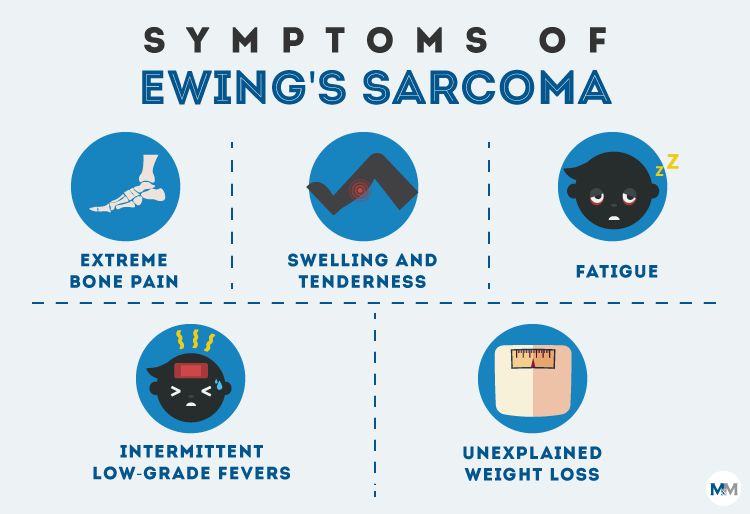
Ewing sarcoma is a less common type of bone cancer, which can also cause bone pain and swelling. It is most often found in young teens. The most common places for it to start are the pelvic (hip) bones, the chest wall (such as the ribs or shoulder blades), or in the middle of the long leg bones.